


Next: About this document ...
Up: Physics in the Space
Previous: Bibliography
- (10 + n)-momentum
- Flat Minkowski spacetime and
- 10-momentum
- Flat Minkowski spacetime and
- absolute parallelism
- The basic geometric and
- action principle
- The action principle and
- active transformations
- Tensor and spinor fields
| Flat Minkowski spacetime and
| Noether's theorem
- anholonomic components
- Tetrads
- anti-de Sitter spacetime
- Flat Minkowski spacetime and
- axial symplectic subgroup
- Subgroups of
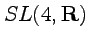
- balance equation
- Minimal coupling and the
- base of a bundle
- Tetrads
- bundle of extended frames
- Maxwell and Yang-Mills fields
- Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa matrix
- Fermions in the Standard
- canonical form
- Connection, soldering, curvature and
- causal influence
- Orbits in
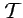 and
and
- causally disjoint
- Orbits in
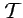 and
and
- charges
- Flat Minkowski spacetime and
- classical geometry
- Critical remarks
- complete solution
- Dynamical variables and symmetry
- composition of transformations
- The operational interpretation and
- cone
- A wedge
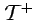 in
in
- connected solution
- Dynamical variables and symmetry
- connection
- A compact formalism
- connection coefficients
- Parallel transport
- connection form
- Connection, soldering, curvature and
- constant solution
- Dynamical variables and symmetry
- contraction of groups
- Subgroups of
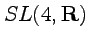
- cosmological constant
- The Einstein-Cartan theory of
- current
- Conserved forms
- curvature form
- Connection, soldering, curvature and
- de Sitter spacetime
- Flat Minkowski spacetime and
- diffeomorphisms
- Dynamical variables and symmetry
- dimensional analysis
- Macroscopic physical interpretation
- Dirac brackets
- Pre-symplectic formalism and double
- Dirac's large numbers problem
- A geometrized scalar-tensor theory
- distinguished point
- Flat Minkowski spacetime and
| Normal field equations and
- double differential forms
- Pre-symplectic formalism and double
- dynamical torsion
- Macroscopic physical interpretation
- energy-momentum
- Flat Minkowski spacetime and
- equity principle
- The equity principle, the
- events
- The spacetime coincidence
- extremal elements
- The Lorentz invariant cone
- feasibility cone
- The Lorentz invariant cone
- feasible infinitesimal transformations
- A wedge
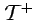 in
in
- fiber
- Tetrads
- foliation
- The spacetime coincidence
- fundamental vector fields
- The basic geometric and
| The operational interpretation and
- gauge field strength
- Parallel transport
- gauge field theories
- Tetrads
- gauge fixing constraints
- Pre-symplectic formalism and double
- gauge transformation
- Dynamical variables and symmetry
- generalized Gauss law
- Conserved forms
- geometric symmetry group
- Dynamical variables and symmetry
- global spacetime interpretation
- The spacetime coincidence
- Hausdorff separation axiom
- The spacetime coincidence
- holonomic components
- Tetrads
- homogeneous space
- Dynamical variables and symmetry
- horizontal degree
- A compact formalism
- horizontal subpace
- A compact formalism
- horizontal tangential equations
- The Einstein-Cartan theory of
- ideal accelerated clock
- The symmetry group
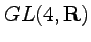
- ideal clock
- The symmetry group
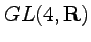
- infinitesimal transformations
- The operational interpretation and
- integrable distribution
- The spacetime coincidence
- integral manifolds
- The spacetime coincidence
- internal degree
- A compact formalism
- internal gauge theory
- Internal gauge theories
- Lagrangian form
- The action principle and
- leaf
- The spacetime coincidence
- left translations
- Flat Minkowski spacetime and
- Lie derivative
- Dynamical variables and symmetry
- local section
- Covariant derivatives and spin
- local spacetime interpretation
- The spacetime coincidence
- Lorentz vertical degree
- A compact formalism
- Mack's principle
- Microscopic considerations and dilatations
- Maurer-Cartan one-forms
- Maxwell and Yang-Mills fields
- Maxwell 2-form
- Conserved forms
- Maxwell equations
- Internal gauge theories
- measurement
- The operational interpretation and
- measurement procedures
- The operational interpretation and
- metricity condition
- Parallel transport
- minimal coupling
- Minimal coupling and the
- minimum time principle
- The equity principle, the
- Minkowski spacetime
- Flat Minkowski spacetime and
- modified geometry
- The Lorentz invariant cone
- moving frame
- Tetrads
- normal field equations
- The action principle and
- normal geometry
- The basic geometric and
- normal limit
- Higher symmetries and a
- orientable manifold
- Tetrads
- parallel transport
- Parallel transport
- passive transformations
- Tensor and spinor fields
| Flat Minkowski spacetime and
- phase space
- Pre-symplectic formalism and double
- physical equivalence
- The spacetime coincidence
- pre-symplectic space
- Pre-symplectic formalism and double
- preparation procedure
- Critical remarks
- primary Lagrangian constraints
- Pre-symplectic formalism and double
- primary local spacetime coincidence
- The spacetime coincidence
- principal fiber bundle
- Tetrads
- procedures
- The operational interpretation and
- projection mapping
- Tetrads
- pseudo-Finslerian space
- The symmetry group
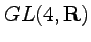
- pseudo-norm
- The symmetry group
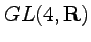
- reciprocal influence
- Orbits in
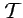 and
and
- regular cubic coordinate system
- The spacetime coincidence
- relational geometry
- The operational interpretation and
- relativistic angular momentum
- Flat Minkowski spacetime and
- relativity principle
- The operational interpretation and
- repère mobile
- Tetrads
- restricted measurement procedures
- Orbits in
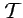 and
and
- restricted measurements
- Orbits in
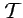 and
and
- reversible infinitesimal transformations
- A wedge
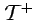 in
in
- Riemann curvature tensor
- Parallel transport
- right translations
- Flat Minkowski spacetime and
- scalar field
- Scalar fields
- scalar-tensor theory
- A geometrized scalar-tensor theory
- secondary local spacetime coincidence
- The spacetime coincidence
- situation
- The operational interpretation and
- soldering form
- Connection, soldering, curvature and
- space of motions
- Pre-symplectic formalism and double
- spacelike submanifold
- Orbits in
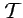 and
and
- spacetime coincidence
- The spacetime coincidence
- spatially localized quantity
- Conserved forms
- spin connection coefficients
- Covariant derivatives and spin
- spin structure
- Tensor and spinor fields
- spinor
- Tensor and spinor fields
- spinors
-
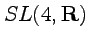 spinors and
spinors and 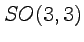
- spontaneous symmetry breaking
- The spinor representation of
- Standard Model
- Fermions in the Standard
- strictly operational interpretation
- The operational interpretation and
- structural group
- Tetrads
- structure coefficients
- A compact formalism
- structure equations
- Connection, soldering, curvature and
- subsolution
- Dynamical variables and symmetry
- substitution rule
- Higher symmetries and a
- symplectic double form
- Pre-symplectic formalism and double
- symplectic form
- Pre-symplectic formalism and double
- tangential field equations
- The action principle and
- teleparallelism
- The basic geometric and
- tetrad
- Tetrads
- time orientable manifold
- Tetrads
- torsion form
- Connection, soldering, curvature and
- torsion tensor
- Parallel transport
- total degree
- A compact formalism
- total dilatations
- Microscopic considerations and dilatations
- transformation procedures
- The operational interpretation and
- transformations
- The operational interpretation and
- trivialization
- The basic geometric and
- vacuum state
- Dynamical variables and symmetry
- vector symplectic subgroup
- Subgroups of
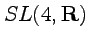
- vertical reflection
- Subgroups of
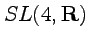
- vertical subpace
- A compact formalism
- vertical tangential equations
- The Einstein-Cartan theory of
- Vierbein
- Tetrads
- wedge
- A wedge
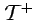 in
in
Marco Toller
2007-11-25